Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
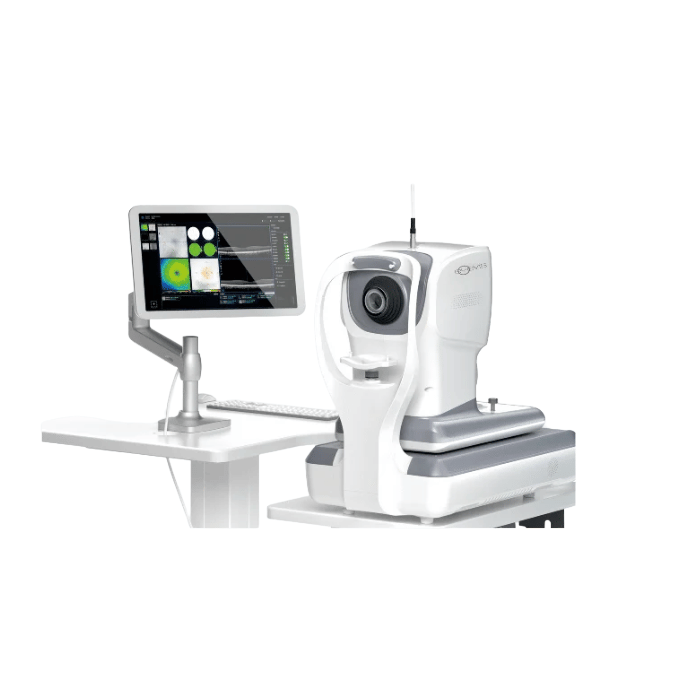
Table of Contents
What is a Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)?
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a noninvasive imaging technique that utilizes near-infrared light to capture high-resolution, cross-sectional images of the eye’s internal structures, particularly the retina. This technology enables eye care professionals to examine the layers of the retina and measure the depth of essential structures, facilitating the diagnosis and management of various eye conditions.
How OCT Works?
OCT operates on principles similar to ultrasound imaging but uses light waves instead of sound. It employs low-coherence interferometry, where a beam of light is split into two paths: one directed at the eye and the other at a reference mirror. The reflected light from both paths is combined to create interference patterns, which are then analyzed to construct detailed images of the eye’s internal structures .
When to Undergo an OCT Eye Test?
An OCT scan may be recommended if you exhibit symptoms indicative of eye diseases or if abnormalities are detected during a routine eye examination. Individuals at risk for age-related eye conditions or other ocular diseases might be advised to include OCT in their regular eye check-ups. This allows for the monitoring of changes over time and early detection of potential issues.
Eye Conditions Diagnosed and Monitored with OCT
OCT is instrumental in diagnosing and managing a range of eye conditions, including:
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Glaucoma
- Macular degeneration
- Retinal detachment
- Macular edema
- Optic nerve disorders
arXiv
Additionally, OCT can assess the anterior segment of the eye, aiding in the diagnosis of corneal diseases and planning for surgeries like cataract extraction .
What Does This Exam Help Diagnose?
A slit lamp examination can help detect various eye conditions, including:
Macular degeneration – A progressive disease affecting the part of the eye responsible for central vision.
Detached retina – A condition where the retina, a crucial tissue layer at the back of the eye, separates from its underlying support.
Cataracts – Clouding of the eye’s lens, leading to blurred or impaired vision.
Corneal injury – Damage to the cornea, the outermost layer of the eye.
Retinal vessel blockages – Obstructions in the blood vessels of the eye, which may cause sudden or gradual vision loss.
Speak with your doctor about what they are examining and any potential eye conditions you may be at risk for.
What to Expect During an OCT Scan?
The OCT procedure is quick and painless, typically completed within a few minutes. You will be seated and asked to place your chin on a support to keep your head steady. Your eye care provider may use drops to dilate your pupils for a better view of the retina. You will then focus on a target while the machine scans your eye. The process is non-contact, and nothing touches your eye during the scan.
Side Effects and Considerations
OCT is a safe procedure with no known risks. If pupil dilation is performed, you may experience temporary light sensitivity and blurred vision for a few hours afterward. It’s advisable to arrange transportation if you anticipate difficulty driving post-examination.
Optical Coherence Tomography Machine - AI EOCT 1
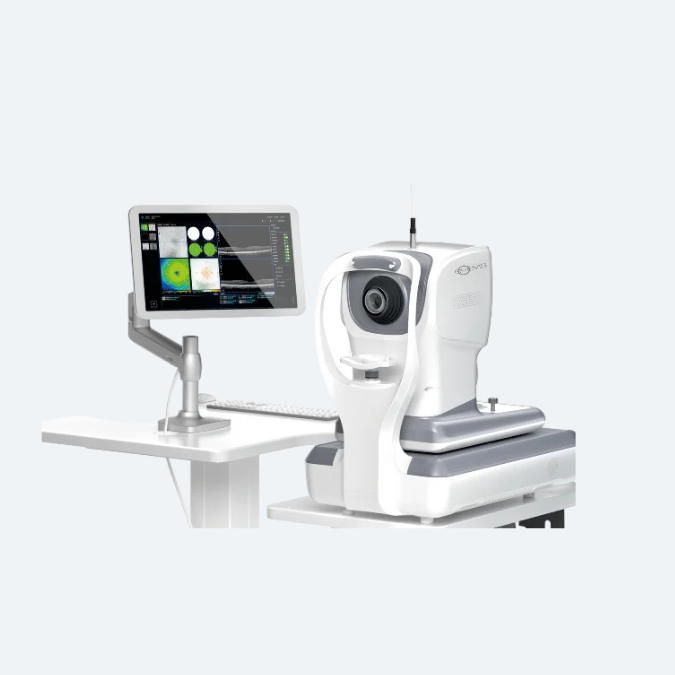
Artificial Intelligence in Optical Coherence Tomography (AI-OCT) is transforming retinal imaging by harnessing machine learning to rapidly and accurately analyze OCT scans. This innovation enhances the detection and management of eye conditions such as glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy, and age-related macular degeneration, leading to improved diagnosis, treatment monitoring, and early intervention. By delivering swift and precise analyses, AI-OCT minimizes human error and supports clinicians in making well-informed decisions.
Lab Medica Systems Pvt. Ltd. is a leading supplier of AI-powered Optical Coherence Tomography Machine in India. Their EOCT 1 system offers high-speed scanning at 86,000 A-scans per second, enabling rapid and accurate detection of retinal diseases like glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy. With advanced AI algorithms, it delivers precise diagnostics, enhancing early detection and treatment planning.

